About Lesson
The WHERE Clause
The WHERE clause is used to extract only those records that fulfill a specified criterion.
The syntax is as follows:
select <column_names> from <table_name> where <column_name> operator value
Example:
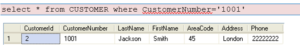
Note! SQL uses single quotes around text values, as shown in the example above.
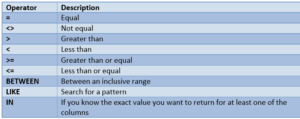
Operators
With the WHERE clause, the following operators can be used:
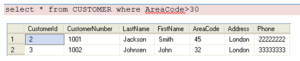
Examples:
LIKE Operator
The LIKE operator is used to search for a specified pattern in a column.
Syntax:
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name WHERE column_name LIKE pattern
Example:
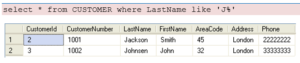
Note! The “%” sign can be used to define wildcards (missing letters in the pattern) both before and after the pattern.
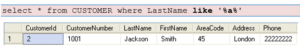
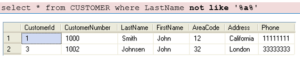
You may also combine with the NOT keyword, example:
IN Operator
The IN operator allows you to specify multiple values in a WHERE clause.
Syntax:
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name WHERE column_name IN (value1,value2,...)
BETWEEN Operator
The BETWEEN operator selects a range of data between two values. The values can be numbers, text, or dates.
Syntax:
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name WHERE column_name BETWEEN value1 AND value2