Variables
The ability to using variables in SQL is a powerful feature. You need to use the keyword DECLARE when you want to define the variables. Local variables must have the the symbol “@” as a prefix. You also need to specify a data type for your variable (int, varchar(x), etc.).
Syntax for declaring variables:
declare @local_variable data_type
If you have more than one variable you want to declare:
declare @myvariable1 data_type, @myvariable2 data_type, …
When you want to assign values to the variable, you must use either a SET or a SELECT
statement.
Example:
declare @myvariable int set @myvariable=4
If you want to see the value for a variable, you can e.g., use the PRINT command like this:
declare @myvariable int set @myvariable=4 print @myvariable
The following will be shown in SQL Server:

Assigning variables with a value from a SELECT statement is very useful.
We use the CUSTOMER table as an example:
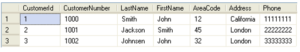
You can assign a value to the variable from a select statement like this:
declare @mylastname varchar(50) select @mylastname=LastName from CUSTOMER where CustomerId=2 print @mylastname
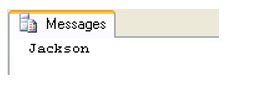
You can also use a variable in the WHERE clause LIKE, e.g., this:
declare @find varchar(30) set @find = 'J%' select * from CUSTOMER where LastName LIKE @find
